GROMACS Peptide Simulation Tutorial
This tutorial will walk you through simulating peptide systems in GROMACS, including custom D-amino acids.
Required Files
Download all necessary files from this Google Drive folder: Simulation Files
If you’re new to GROMACS, consider starting with this basic tutorial on lysozyme.
Custom D-Amino Acids
To simulate D-amino acids:
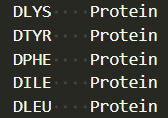
- Include a
residuetype.datfile to introduce your new residue into the force field. - This file must be in the same directory as your system-building scripts.
- Use a 3- or 4-letter code (e.g.,
DTYR,DPHE) that matches your Avogadro output.
Example:
Step 1: Build the Amino Acid (Avogadro)
Follow this Avogadro tutorial to build and save your peptide (e.g., dkyfilinvert.pdb).
Step 2: Load GROMACS on Rivanna
Open a terminal on Rivanna and load the required modules:
module load gcc/11.4.0 openmpi/4.1.4 gromacs/2023.2
Step 3: Convert PDB to GROMACS Format
Convert your .pdb file to .gro using:
gmx_mpi pdb2gmx -f dkyfilinvert.pdb -o dkyfil.gro
Choose these options when prompted:
- Force field:
1(CHARMM) - Water model:
1(TIP3P) - Terminal capping:
2(CT2 to amidate Leu C-terminus)
Step 4: Create a 3D Peptide Grid
Use genconf to create a randomized peptide box (e.g., 4x4x4 = 64 peptides):
gmx_mpi genconf -f dkyfil.gro -nbox 4 4 4 -rot yes -dist 1.6243 2.5864 1.8081 -o dKYFIL_64_box.gro
-rot yes: Randomly rotates each peptide.-dist: Distance (in nm) between peptides in x, y, z directions.
Step 5: Solvate the System
Add water and generate a topology file:
gmx_mpi solvate -cp KYFIL_64_peptides.gro -o KYFIL_64_peptides_solvate.gro -p topol.top
Step 6: Prepare for Ion Addition
Generate the machine-readable .tpr file:
gmx_mpi grompp -f ions.mdp -c KYFIL_64_peptides_solvate.gro -p topol.top -o ions.tpr
Step 7: Add Ions (Neutralize & Set 150 mM Salt)
gmx_mpi genion -s ions.tpr -o dkyfil_64_peptides_solvate_ions.gro -p topol.top -pname NA -nname CL -neutral -conc 0.15
When prompted, select group 13 (SOL) to replace water with ions.
Step 8: Energy Minimization
Create the energy minimization input:
gmx grompp -f minim.mdp -c KYFIL_64_peptides_solvate_ions.gro -p topol.top -o em.tpr
Then run the following SLURM script to perform energy minimization:
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --nodes=7
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=36
#SBATCH --mail-user=[computingID]@virginia.edu
#SBATCH --mail-type=END,FAIL,TIME_LIMIT
#SBATCH --time=3-00:00:00
#SBATCH --partition=parallel
#SBATCH -A [allocation]
#SBATCH -o minimize.out
module purge
module load gcc/11.4.0 openmpi/4.1.4 gromacs/2023.2
gmx mdrun -v -deffnm em
Step 9: Molecular Dynamics (MD) Run Prep
Generate the MD .tpr file:
gmx grompp -f md.mdp -c em.gro -r em.gro -p topol.top -o md.tpr
Then submit this SLURM job script to run the full simulation:
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --nodes=7
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=36
#SBATCH --mail-user=[computingID]@virginia.edu
#SBATCH --mail-type=END,FAIL,TIME_LIMIT
#SBATCH --time=3-00:00:00
#SBATCH --partition=parallel
#SBATCH -A [allocation]
#SBATCH -o dynamicrun.out
module purge
module load gcc/11.4.0 openmpi/4.1.4 gromacs/2023.2
gmx mdrun -v -deffnm md
You're Done!
Your simulation is now running. When complete, you'll have .gro, .xtc, and .edr files ready for analysis.